Introduction
As an owner of a product manufacturing company, you must know how to calculate the cost of goods sold. Unfortunately, many industrialists have either no knowledge or an unclear understanding of it.
The result is inefficient inventory, poor financial health, and an inaccurate pricing structure. In contrast, if professionals are familiar with COGS, it is easier for them to manage costs and overall profitability.
Calculating the correct Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is crucial for determining the correct product price. It enables business professionals to make informed decisions and adjust costs to align with the company’s profit. Thus, production companies can easily meet their goals while knowing their cost of goods sold (COGS).
Our words will help you determine the real meaning of the cost of goods sold. Along with it, you’ll also identify the COGS formula and a guide on how to calculate the cost of goods sold.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The full form of COGS is the Cost of Goods Sold.
- COGS accounts for the costs of raw materials, labor, and overall manufacturing overhead.
- Indirect costs, such as sales, marketing, and administrative expenses, are not part of the cost of goods sold.
- A high COGS indicates a low profit margin, while a low COGS refers to a high profit margin.
- Inventory levels directly influence the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), and they decrease as inventory levels increase.
What Is the Cost of Goods Sold?
The Cost of Goods Sold (also known as Cost of Sales) is defined as direct expenditure related to the goods manufacturing in a particular company. Costs related to materials and labor are covered under the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). In contrast, sales force costs and distribution costs are not included in this category.
COGS is useful for determining a company’s ability to manage direct production costs. Professionals can make an informed decision regarding the cost while understanding the cash flow.
What Are the Costs COGS Includes?
COGS covers labor costs, material costs as variable costs, and overhead expenses like fixed costs.
The cost of goods sold consistently accounts for the total cost of goods produced. The products are sold during a specific period. The cost factors considered are –
-
- Labor cost
- Material cost
- Indirect cost
- Shipping cost
- Direct production cost
- Factory overhead
💡Do You Know?
The beauty industry typically possesses a COGS range of 5% to 30% according to Forbes.
What Is the Cost of Goods Sold Formula?

The formula of COGS is key to determining the cost of goods sold straightforwardly. All you need is a ready-to-use figure for starting inventory, ending inventory, and purchase value. This will ease the calculation.
How to calculate the cost of goods sold? Many business owners lack familiarity with the proper procedure. Well, it all requires familiarity with the cost of goods sold formula mentioned below:
Cost of Goods Sold = Starting Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory
Now, let’s understand the calculation through the cost of goods sold example as explained below.
Cost of Goods Sold Example
Suppose you are running a manufacturing company and it possesses the following values:
Inventory value at the beginning of the year: $50,000
Inventory value at year-end: $8,000
Cost of purchase: $5,000
According to the COGS formula, COGS is an outcome obtained by subtracting the ending inventory from the total sum of the starting inventory and the purchase value. So, putting all values in the formula, we get the result as:
COGS = ($50,000 + $5,000) – $8,000
COGS = $47,000
Therefore, $47,000 represents the cost of goods sold that the business incurs. In the above example of the cost of goods sold, we have explained the calculation.
Why Is the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) So Crucial?
After reviewing the COGS definition, it is also necessary to determine why the cost of goods sold is so important. The answer has been described in the form of the following points:
Determine Profitability
Companies can easily determine their profitability level. They can predict which product is yielding more profit for the company in sales. Also, the company can adjust the price of the product when it’s not meeting the profitability level.
Expense Analyse
The COGS analysis provides a clear understanding of all the costs involved in the manufacturing process. Therefore, professionals can easily identify which area has the potential to lower the cost. In this way, it helps to track the expenditure.
Price Settlement
Business owners can set a competitive cost by using the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) method. A high COGS indicates a low price. Therefore, it is easy to determine the desired profit margin of the product by knowing the COGS cost.
Inventory Management
Identifying COGS helps business professionals identify slow-moving inventory. Professionals can easily reduce storage costs. Additionally, it is easy to identify the stock level, which helps to overcome overstocking or understocking conditions.
Taxation
The correct COGS calculation enables companies to easily manage and comply with tax regulations. It is worth noting that incorrect COGS data can lead to complications in taxation, ultimately resulting in financial losses for the company. Therefore, it is crucial to calculate the correct COGS accurately.
You Can Win Half the Business Success With Clean Estimation
Do you want to experience it? Try Moon Invoice, which commits to accuracy and speed on every estimate.
What Are the Limitations of COGS?
While COGS is a valuable metric, it also possesses some drawbacks that affect its use. Determining the current market value in COGS can be challenging or impossible. The reason is that it relies on past data, which makes it happen.
Additionally, indirect expenses such as administrative costs and marketing expenses are not included in COGS, although they impact profitability. Due to several variable factors, the costs of goods sold are prone to errors. A wrong COGS can directly impact the results of business operations. It may not be so worthy for service-based companies as for product-based ones.
Tips for COGS Calculation
When considering the question of how to calculate the cost of goods sold, it is essential to keep the following points in mind.
-
- Determining direct & indirect costs is important for the efficient outcome. You must clearly distinguish between direct and indirect costs.
- Choosing the right inventory valuation method is crucial. Try to use the same method every time, as results may vary when switching methods.
- Conduct inventory audits at regular intervals.
- Utilizing accounting software enables the gain of insight into the production cost while automating inventory management.
- The supplier cost impacts the cost of goods sold. Regular monitoring of these changes helps establish a fair pricing structure.
Cost of Goods Sold Formula for Retailers

Retailers use the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) to determine the direct cost of the products they sell. The cost is directly associated with the inventory. Include material costs, supply expenditures, and sales tax when thinking about how to find the cost of goods sold.
COGS is crucial for retailers to determine the direct cost of selling products. Therefore, performing an accurate COGS calculation is necessary. For retailers, the overall cost is directly related to inventory.
The cost of goods sold formula that applies to retailers:
Cost of Goods Sold = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory
Here,
Beginning Inventory: The initial value of the inventory at the start of the accounting period.
Purchase: The total cost of inventory items purchased during a specific accounting period.
Ending Inventory: The inventory value is considered at the end of the accounting period.
Cost of Goods Sold Formula for Manufacturers
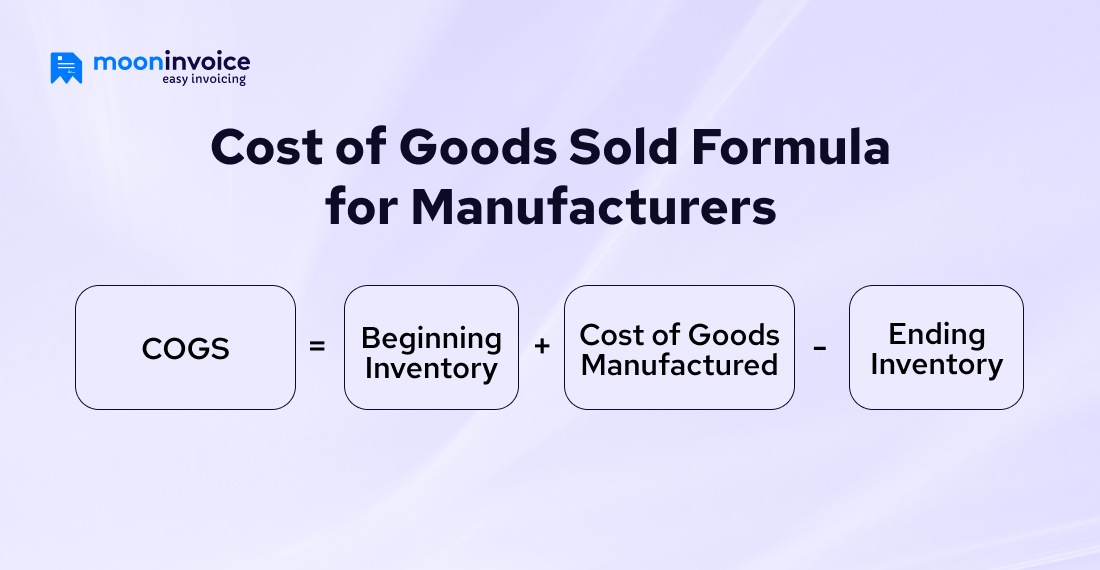
Manufacturers can effortlessly optimize the production costs. The manufacturing overhead, raw materials, and labor costs are included in the calculation.
The formula for calculating COGS for manufacturers
COGS = Beginning Inventory + Cost of Goods Manufactured – Ending Inventory
Here,
Beginning Inventory: The inventory value at the beginning of the accounting period.
Cost of Goods Manufactured: The cost of goods manufactured encompasses labor, materials, and manufacturing overheads.
Ending Inventory: The inventory value at the end of the year or accounting period.
Revenue Cost vs Cost of Goods Sold
There is a difference between revenue cost and cost of goods sold based on their purpose.
Here is the comparison table.
| Revenue Cost | Cost of Goods Sold |
|---|---|
| Cost of revenue refers to the direct costs incurred during revenue generation. | Cost of goods sold refers to the costs that are associated with producing the goods sold. |
| It has a broader scope than COGS. | COGS is quite narrow as it is only related to production. |
| It is highly common in service-based and technical companies. | It is common in manufacturing units and product-based companies. |
| It includes COGS, along with shipping charges, commission, marketing, and other costs. | COGS comprises labor costs, material costs, and other manufacturing expenditures. |
Operating Expenses vs Cost of Goods Sold
Operating expenses and COGS are different from each other in terms of their purpose. Operating expenses are more aligned with the cost of business operations. At the same time, COGS is more closely aligned with the cost of goods sold in production. Here are more comparison points:
| Operating Expenses | Cost of Goods Sold |
|---|---|
| Operating expenses refer to the costs associated with day-to-day business operations. | COGS represented the expenditures associated with product manufacturing. |
| It covers rent, utility expenditures, insurance, and marketing. | It reflects all the costs involved in the manufacturing of goods. |
| Operating expenditure includes fixed and variable costs. | COGS covers variable costs based on sales or production volume. |
| It applies to all businesses regardless of their nature & size. | It is primarily applicable to manufacturing companies that produce goods or products. |
💡Take a Look at: 👉
What Are the Different COGS Accounting Techniques?
To determine the inventory cost, there are different methods of COGS accounting. Professionals must select the method based on business conditions and the nature of the inventory. In general, there are three COGS accounting methods: FIFO, LIFO & weighted average cost. Yet, a special identification process is useful for unique products. You can find the difference between FIFO and LIFO here.
1. First In, First Out (FIFO)
In this method, products are sold in the order in which they are produced. The product that is produced first is sold first. The first-in, first-out (FIFO) accounting method for the cost of goods sold (COGS) is ideal for products with a short-term life.
2. Last In, First Out (LIFO)
LIFO is in contrast to FIFO, which is the method of selling products first that were lastly added to the inventory. This method is applicable to expensive products and also leads to a higher COGS amount. The net income slows down over time.
3. Weighted Average Cost
In this method, a uniform cost is assigned to each inventory unit regardless of its purchasing date. This uniform cost is obtained by dividing the total cost of goods available by the total units. This method is commonly used by agricultural industries or manufacturing units that produce large-scale products.
4. Special Identification Process
This method tracks the item’s specific cost as it is sold from inventory. The average cost, or the assumed cost, doesn’t work here. This method is applicable to high-priced items, such as automobiles, jewelry, and real estate projects.
Is It Hard to Manage Your Expenditure?
Thousands of business professionals are managing their business expenses smartly with Moon Invoice. Ready to be a part of it?
What Are the Best Approaches to Control the Cost of Goods Sold?
How to calculate the cost of goods sold? Thus far, we have acquired sufficient knowledge on the subject. However, you must also be aware of the best practices to reduce the COGS, mentioned below:
Choose Offshore Manufacturing
In the USA, manufacturing is quite expensive. That’s why opting to outsource the manufacturing process is a better option. Companies can deal with countries where labor costs are cheap & affordable. Although it may present some challenges, such as currency fluctuations and customs duties, it remains a viable approach worth considering.
Say No to Cost Waste
A high waste of raw materials could be an indication of an inefficient manufacturing process. This waste is directly impacting COGS and increasing it. One way to manage waste is to reuse it within the production process.
Opt for Lower Cost Materials
COGS covers material costs, so will it be possible to have lower COGS with high raw material costs? Definitely not!
Choosing the low-cost material is another method of reducing the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). But the condition is that you must replace the material smartly in your product. Ensure that the inexpensive material does not compromise the quality of your product. Once the quality of the material fails to win the customer’s heart, it’ll result in a significant drop in sales. Therefore, always analyze the alignment of the material with your client’s expectations.
Incorporate Automation
Automation is a significant factor in reducing the cost of goods sold (COGS). It directly affects labor costs and significantly reduces them. As a result, companies can avail of the optimal COGS. Replacing machines with labor also cuts down errors. Moreover, you must also convince your suppliers to use automation. This will reduce the supplier cost, ultimately lowering your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Use Negotiation Power
Never stick to one supplier. You may find many suppliers and varieties of suppliers with costs that range in the market. Contact different suppliers and get their costs. Choose the price that best fits your budget after comparing the costs.
Final Remark
How to calculate the cost of goods sold? We have presented the right approach to it. Determining the cost of goods sold is crucial; a lower COGS value indicates a higher profit margin for the company. Therefore, business owners need to keep this cost under control while managing it efficiently. Handling inventory, optimizing the supply chain, and minimizing waste are key methods for reducing costs.
Step up your financial game with Moon Invoice. It is one of the fantastic platforms to manage your bookkeeping while leveraging automation. Enhance your work with accuracy and speed. Try it for free!














