How do you protect your business from fraud or scams? Currently, invoicing fraud has become a growing concern for businesses, regardless of their size. Since internet access and remote work have become normalized, the risk of fraudulent online activities has increased.
According to a 2021 FBI report, there were more victims of crimes such as phishing, non-payment/non-delivery, personal data breach, identity theft, and extortion than any other crime in 2021. Victims of phishing topped the list with 323,972. So, even though technology is evolving, the hindsight is that the vast resources available on the internet make scammers more active.
Now, the biggest question is: what should you do? How will you protect your business from invoice fraud?
In this blog, we will explore how you can identify fake invoices, along with types of invoice fraud, and how you can avoid all these by implementing small steps.
Let’s dive in.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Invoice fraud occurs when scammers manipulate billing processes through fake or duplicate invoices.
- Slightly altered payment details, vague invoice descriptions, and unmatched invoice amounts are common signs of fake invoices.
- Invoice fraud can damage a business’s reputation, disrupt operations, and lead to legal consequences.
- Following a proper invoice matching process for all invoices, including those from new vendors, helps prevent fraud.
- Using invoicing software with real-time tracking, cloud storage, and security features can help protect businesses from invoice fraud.
What is Invoice Fraud?
Invoice fraud is a practice in which fraudsters create fake invoices, submit false invoice data, or manipulate invoices to achieve financial gain. When businesses fail to detect these fraudulent activities, they fall in the trap of invoice fraud.
There are multiple ways to commit invoice fraud, which is mainly done by scammers who impersonate legitimate vendors, cybercriminals who use phishing tactics, or dishonest employees within the organization.
The most common forms of invoice fraud include:
- Fake Invoices
- Duplicate Billing
- Inflated Charges
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams
To secure your business from invoice fraud, implement strict protocols and verification processes. Fraudsters always look for a weak link in their target business. Improper finance, lack of verification, and human errors are the primary reasons for invoice fraud.
Tired of Second-Guessing Every Invoice?
Stop invoice fraud before it starts. Switch to Moon Invoice and gain total control over your billing.
How to Identify Fake Invoices?

Early detection of fake invoice scams has bigger benefits as it saves you from financial losses. In every fake invoice, there is always one sign or something unusual you can notice.
Below are the signs of a fake invoice fraud:
1. Invoices from Unverified Vendors
Receiving an invoice from an unrecognized vendor is a red flag. Unknown invoices must undergo proper validation before payment is approved.
2. Slightly Altered Vendor Details
Sometimes, scammers act smart and change minor details of the invoice, such as the email address, phone numbers, and bank account information, to make the invoice look legitimate.
3. Generic Descriptions of Goods/Services
A legitimate invoice comes with a proper breakdown of products or services with their description, quantities, and prices. However, fake invoices mostly use vague descriptions like “Professional fees” or “Additional charges.”
4. Pressure to Process Payment Quickly
An unusual urgency, asking for bank account details, or forcefulne ss to pay as soon as possible, these kinds of behaviours from the vendor could indicate fraud activity. Legitimate vendors provide a reasonable timeframe.
ss to pay as soon as possible, these kinds of behaviours from the vendor could indicate fraud activity. Legitimate vendors provide a reasonable timeframe.
5. Unmatched Invoice Amounts
Any invoice amount that doesn’t match the agreed-upon terms or is higher than usual requires proper investigation before payment is made. Generally, invoice scams occur when these hidden fees go unnoticed.
6. Duplicate Invoice Numbers
If you receive the same invoice more than once with slight changes in the invoice number, that also indicates fake invoice practices. Note the numbering sequence and consider using an automated invoice matching software to avoid invoice scams.
7. Suspicious Payment Instructions
A sudden change in bank details without prior notice is a huge concern. Contact the vendor directly with official contact details and clarify if any such changes have been made.
Types of Invoice Fraud

Invoice fraud can take various forms. It can be from scams outside of your business or even internal scams, such as a dishonest employee working to compromise internal security access.
Here are the most common types of invoice fraud you should be aware of:
1. Fake Vendor Invoices
This type of fraud happens when fraudsters send invoices for goods or services that were never provided. Fake vendor invoices look very professional, and a lack of proper verification can lead to getting trapped in fake vendor invoice fraud.
How to prevent it?
- Verify every invoice before making payments (for both old and new)
- Match the invoice with the Purchase order and the contract
2. Duplicate Invoices
Duplicate invoices are one of the easiest invoice scams. Here, a fraudster submits the same invoice multiple times, hoping it gets paid twice. Not using invoice tracking systems or making clerical errors opens the door to falling victim to duplicate invoice fraud.
How to prevent it?
- Must use an automated software solution to identify duplicate invoice numbers.
- Do periodic audits of vendor payments
3. Inflated Invoices
This type of vendor fraud occurs when a legitimate vendor suddenly hikes prices, increases quantities, or adds hidden fees. Scammers modify the existing invoice with additional information and expect the business may not notice these minor invoice discrepancies.
How to prevent it?
- To avoid duplicate payment fraud, you must maintain records of past orders and transactions.
- Large invoice amounts and unusual invoices must go through a review process.
4. Internal Employee Fraud
This type of invoice fraud is a huge setback for any business. A dishonest employee working with vendors to submit fake invoices comes under this category. Since the employee is part of your business and works within the company, it becomes tricky and challenging to detect fraud.
What can you do?
- No employee should have full control of the invoice and payments. Switch duties more often to avoid payment fraud.
- Schedule surprise audits to identify suspicious vendor relationships.
5. Business Email Compromise (BEC) or CEO Fraud
These are invoice email scams where the scammer hacks or spoofs a CEO’s or vendor’s email to request urgent payments. They impersonate higher-level senior executives (such as CEOs, CFOs, or CTOs) or even a well-known supplier.
How to prevent it?
- If the payment request is coming from higher authorities, do verify once with either a call or other options.
- Implement two-factor authentication for payment approvals.
6. Overpayment Scams
Overpayment is another smart tactic fraudsters use to get money. What happens here is the fraudster will send a fake invoice and “accidentally” overpay. Then they will ask for a refund and request you to send the amount to a different bank account.
How to prevent it?
- Check every payment before issuing refunds.
- Verify with the vendor over the phone and ensure refunds are sent to the original source.
7. Shell Company Invoicing
This type of fake invoice is operated by setting up a fake company and then submitting invoices for non-existent services. Sometimes these invoices appear very legitimate, but in reality, they have no business history or activity.
How to prevent it?
- Always verify new vendors with their business registration number.
- Don’t approve payments for vendors with whom you have no prior history until verification is complete.
Implement automated invoicing software like Moon Invoice to reduce the risk of fraud. It helps you detect discrepancies and prevent unauthorized payments.
What is the Impact of Invoice Scams in Businesses?

Invoice scam can completely ruin a company’s reputation, finances, and overall operations. The impact could be massive. In some cases, it may threaten the stability of the company.
Below are the impacts of invoice scams on businesses:
1. Financial Losses
Financial losses are the most affected and concerning part of invoice scams. Generally, the goal of every scammer is to steal money, isn’t it?
When fake invoices are approved and paid without verification, it leads to direct monetary losses with a very low probability of recovery. For international payments, the situation worsens, and the chances of recovery are negligible.
2. Operational Disruptions
If your business is affected by a fraudulent invoice, even once, the road to fully recover to normal is never easy. You will look for suspicious activities with supporting documents, a close look at the accounts payable process, and internal audits, which will divert your attention from daily operations.
It becomes difficult to trust new vendors again, and it eventually affects the supply chain.
3. Reputational Damage
When your customers or business partners find out that the company is dealing with invoice scams, it is clear that they will lose trust in the company. The finance system will be questioned. Falling for invoice scams results in damaged relationships with vendors, investors, and stakeholders.
If it is an internal employee fraud, the company’s brand image could be affected.
4. Legal and Compliance Risks
Approving fraudulent invoices and making payments could put your business at risk of tax-related issues and legal complications. Invoice scams involve identity theft or cybercrime, and in such cases, it is mandatory to file reports with the law enforcement agency.
Businesses in regulated industries, such as finance or healthcare, could face penalties or fines for falling victim to a fraudulent invoice.
Is Your Invoicing System Leaving You Exposed?
Say goodbye to shady vendors and suspicious bills. Moon Invoice gives you control.
Avoid Invoice Fraud with Moon Invoice
Combating invoice fraud requires an automated solution. In today’s rapidly growing business world, your business needs an invoicing solution that is secure and transparent.
With Moon Invoice, you can prevent invoice fraud and safeguard the financial data of your business with secure cloud storage and 256-bit SSL encryption. No more phony invoice past scams!
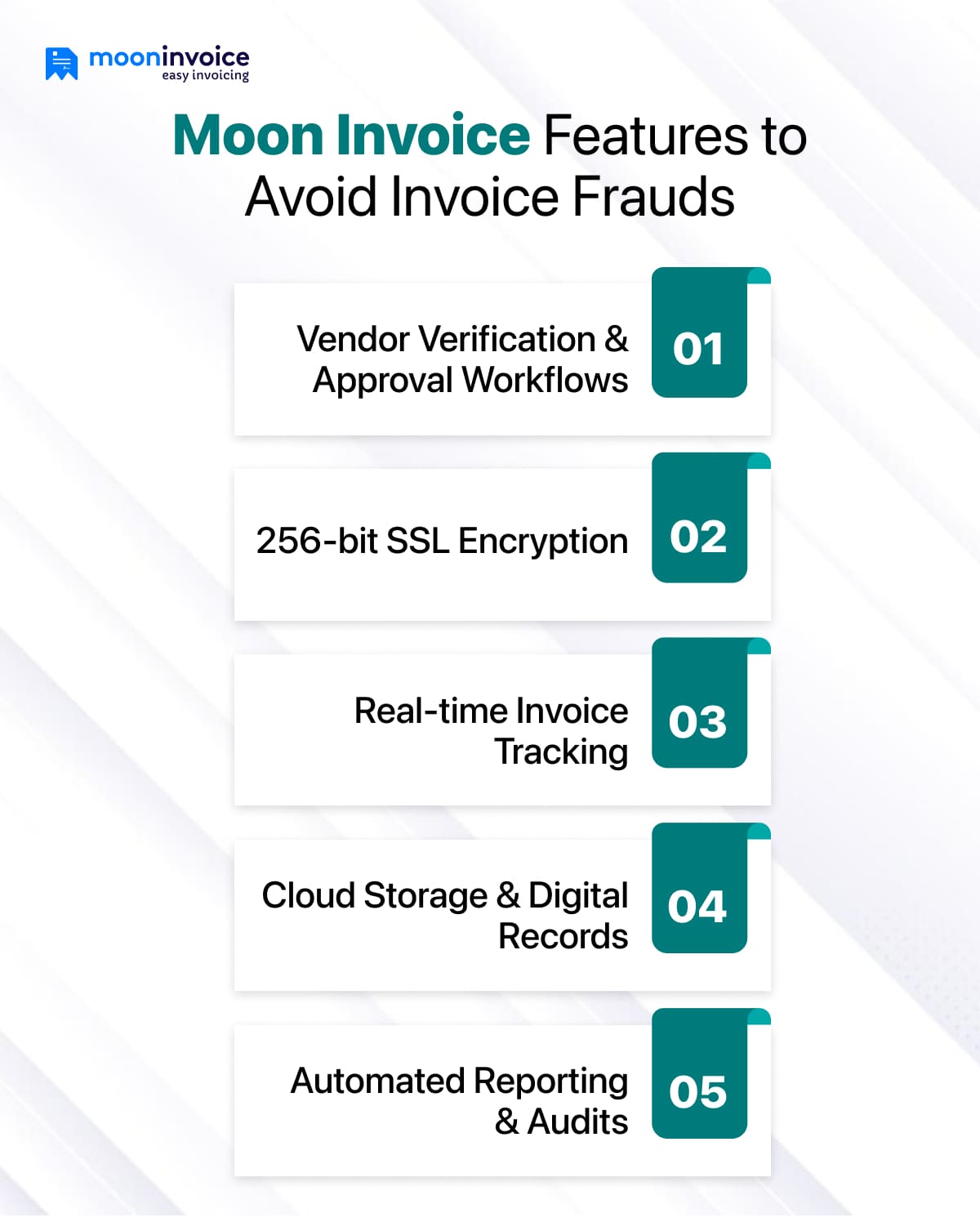
Here’s how Moon Invoice helps you:
- Vendor Verification & Approval Workflows: Set up approval workflows to ensure each vendor detail is verified before processing payments.
- 256-bit SSL Encryption: A strong encryption method that ensures enhanced data protection.
- Real-Time Invoice Tracking: Track invoices, match them with purchase orders and delivery receipts to avoid invoice fraud.
- Secure Cloud Storage & Digital Records: Store your invoices in the cloud and retrieve them at any time to detect inconsistencies and review past vendor transactions.
- Automated Reporting & Audits: Helps you identify suspicious transactions and ensure compliance with financial policies.
Conclusion
Why does invoice fraud happen more frequently? A simple answer is not tracking invoices regularly. Even experienced accounts payable teams fall victim to scams when they don’t follow security measures.
So, what to do? Is it that complex to track invoices? Not really. With invoicing software like Moon Invoice, you can streamline invoicing, enhance transparency, and automate fraud detection to protect your finances.
Don’t let invoicing fraud disrupt your business—equip yourself with the right tools and stay ahead of fraudsters with Moon Invoice.
Book a free demo now!














