Operating Income Definition
Operating income refers to the company’s profit earned after deducting all the operating expenses from the gross income.
Operating income is a key metric for understanding a business. Why? It shows the core income generated by the business’s core operations. Simply put, it means you have a clear view of the profit generated by your business’s core operations.
However, the central issue is that professionals are uncertain about how to calculate operating income. Ultimately, it results in poor decision-making, misunderstanding the core structure, and difficulty communicating with bankers and investment professionals.
If you have little or no understanding of operating income, this is the right opportunity for you. Here’s the guide on the same. Our blog will help you understand operating income from the start, including its core meaning, formula, calculation, importance, and more.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Operating income is the company’s profit earned after deducting operating expenses from revenue.
- A company with high operating income generally demonstrates strong operational efficiency.
- Operating income and earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are the same.
- Understanding how to calculate operating income is essential for business leaders and investors.
- Operating income excludes non-operating income, taxes, and capital structure expenses.
- Operating income is recorded at the bottom of a company’s income statement.
💡Fact to Know:
Google reported operating income of approximately 37.12 billion U.S. dollars in the third quarter of this year, as per the
Statista report.
What Is Operating Income?
Operating income is a financial metric that represents a company’s profit after deducting operating expenses from gross profit. Professionals assess whether the business is generating sufficient profit from its core activities.
In other words, operating income focuses on the core income and expenses associated with its operations.
Investors, bankers, and lenders always focus on the operating income metric before investing. This gives them a clear picture of your company’s operational efficiency. They take further action by analysing the status of operating income.
What Is the Formula to Calculate Operating Income?

The operating income formula is the right key to compute operating income. Without this, it is impossible to find the correct figure & analyze your company’s core operations’ contribution to profit. You can straightforwardly use the formula to calculate operating income. All you want are the accurate values of the equation’s components.
Here is the general formula for operating income, often known as the top-down approach.
Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Extending this formula, we get:
Operating Income = Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
Where,
Gross Profit –
Gross profit is the income a company retains after subtracting the cost of goods sold from total revenue. It is calculated as below:
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
COGS –
It is also known as a direct cost. Cost of Goods Sold refers to the costs the company incurred in producing the product and delivering the service. Thus, it covers the entire manufacturing cost.
Operating Expenses –
It is also known as an indirect cost. Operating expenses are the costs associated with a company’s operations. Utility bills, office rent, and other costs incurred during business operations fall under this category.
Alternatively, there are two other formulas to calculate operating income in expanded form:
1. Using EBITDA
Operating Income = EBITDA−Depreciation−Amortization
Here,
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) – Reflects the performance before non-cash expenses.
Depreciation and amortization – The operating expenses that are related to intangible assets.
This formula is applicable only when EBITDA covers only operating activities.
2. Bottom-up Approach
Operating income = Net Income + Interest Expense + Tax Expense
Here,
Net Income – The final profit that the company gains after deducting all expenses from the total revenue.
Interest Expense – The cost that the company pays on borrowed funds, like bonds, loans, or credit lines.
Tax Expense – The Amount that the company owes to the local government and is referred to as liabilities.
Is Financial Management a Never-Ending Struggle?
Get your finances perfectly managed with Moon Invoice. 99% accuracy on every transaction.
Operating Income Percentage Formula
The operating income percentage formula is also known as operating margin. It shows the portion of the company’s revenue that can be converted into operating profit. It also reflects the profit the company earns from its core operations per unit of revenue.
Operating Income Percentage (%) = Operating Income ÷ Revenue x 100
Where,
Operating Income = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) – Operating Expense
Total Revenue = Gross income before the deductions
The higher the operating income percentage, the better the cost control, and the stronger the operational profitability. In contrast, a lower operating income percentage refers to pricing inefficiencies.
How to Calculate Operating Income? Step-By-Step Guide
With a deep understanding of the operating income definition, we can now calculate it. Most professionals prefer the top-down approach, so let’s use the same approach in the calculation.
1. Gathering Values
So, how do you calculate operating income? The initial approach is to collect data. First, professionals need to gather the values for revenue, COGS, and operating expenses. Figure out the amount of revenue the company generated, and how much was spent on products. Also, determine the amount of expenses the company incurs in its operations. You can refer to the company’s financial statements or contact the accounting department.
2. Put in the Formula
Once all values are collected, apply them to the operating income formula. As the common method is a top-down approach, professionals simply need to put the data in the following formula:
Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Subtract the operating expense from the gross profit to get the final value.
3. Verification & Analyses
Once you find the final result, use it to analyse the business operations. It is useful for identifying which expenses can be reduced and for identifying further process improvements. Beyond this, it is also useful in attracting investors.
Operating Income Examples
Here are real-life examples to demonstrate your better understanding of how to find operating income.
Example 1
Let’s understand operating income with a real-life example that demonstrates the flow. Suppose a kitchenware manufacturer produces kitchen products. It spends some dollars producing a product, known as COGS. This includes raw material purchases and direct labor costs.
The company incurs operating expenses, including rent, utility bills, and wages. The company observes the following metrics:
Revenue: $100,000
COGS: $20,000
Gross profit: $100,000 – $20,000 = $80,000
Total Operating Expenses: $20,000
Operating Income = $80,000 – $20,000 = $60,000
So, $60,000 is the company’s core business revenue.
Example 2
Let’s review the operating income calculation using another example: a financial consulting services company, Skyline. Since the business is not involved in manufacturing, service costs will be used instead of goods production costs.
This means the company will incur all costs associated with delivering the service. This covers software tools, consulting fees, and employee salaries. Additionally, it will cover all operating expenses, including office rent, depreciation expense, and marketing & advertising costs.
Revenue: $90,000
Service cost: $20,000
Total Operating expenses: $20,000
Gross profit = Revenue – Service cost
$90,000 – $20,000 = $70,000
Operating income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
$70,000 – $20,000 = $50,000
The financial consultancy firm earns $50,000 from its core operation.
💡Fact at a Glance:
Operating income can be equal to net income if the company doesn’t have any expenses related to interest, taxes, or non-operating gains or losses.
How to Increase Operating Income?
So far, we have understood how to calculate operating income. But you might also think, “Can I boost my business’s operating income?” The answer is Yes!
Here are the key approaches to increasing your business’s operating income.
Lowers the Raw Material Costs
Securing low-cost raw materials is a common practice. Professionals can negotiate prices with the vendors. Additionally, you can conduct market research and compare prices. Opt for budget-friendly raw materials without compromising quality.
Increase Sales to Existing Customers
It is generally better to increase sales to existing customers than to seek new ones. This is because acquiring new customers is more expensive, with marketing and promotion as the primary cost drivers. Utilize the Customer Relationship Management that helps to understand customers’ behaviour and needs by providing better insights.
Eliminating the Low-Performing Products & Services
Not all products & services perform equally well or yield a good profit. You must analyze and discontinue all such products & services that come under this category. This will reduce your expenses and help you achieve a high operating income.
Opt for Automation
Automating the time-consuming manual process can also reduce costs and increase profitability and productivity. For instance, professionals can use invoicing software to automate invoicing. This reduces process time and costs associated with manual processes.
Reducing Labor Inefficiencies
Improving labor efficiency is an effective strategy to increase operating income. You can optimize the staff schedule and track the productivity per job. Also, providing proper training can improve productivity, thereby increasing revenue.
Common Challenges in Reporting Operating Income
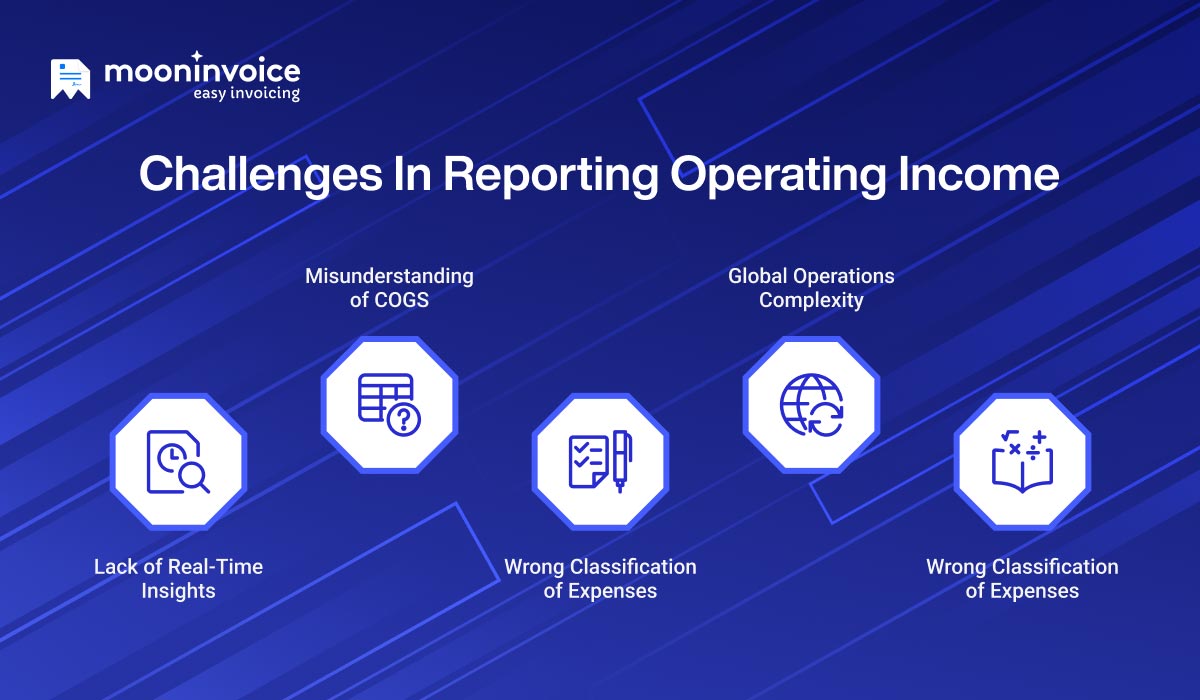
There are some challenges in managing operating income. These issues further lead to poor decision-making and misleading insights. Professionals often face the following challenges when reporting operating income.
Lack of Real-Time Insights
Due to manual processes, professionals don’t receive up-to-date information in real time. The outdated data further undermines the process. The best solution is to utilize the automated tools that speed up the process while maintaining accuracy.
Misunderstanding of COGS
Often, professionals don’t understand or manage COGS properly. Often, they conflate overhead costs and operating expenditures with direct production or services. This reflects an incorrect cost of goods sold status, which affects operating income.
Wrong Classification of Expenses
Sometimes expense classifications are incorrect, further complicating matters for professionals. This type of expenditure misclassification can lead to an inaccurate view of the company’s core operating performance. This further leads to incorrect budgeting and cost-control decisions, negatively impacting the overall process.
Global Operations Complexity
Different nations have different currencies, taxation laws, and accounting standards. Therefore, it makes it difficult to understand and report operating income for multinational corporations. Exchange rate fluctuations further complicate matters and make it difficult to present a clear picture.
Variation in Accounting Methods
Different businesses use different accounting methods, which further affect the reporting of operating income. The time at which the company recognizes the sales revenue is also the timing of operating income.
💡Pro Tip:
Always analyze operating income monthly. This helps to spot pricing issues and margin erosion at an early stage.
Why Is Accurate Operating Income Crucial?
What is operating income? This is part of the story, but why is it crucial? You must be aware of it. Accurate operating income is crucial for the business because it is a key indicator of profitability from core operations. It indicates the business’s ability to generate profit from its core operations. As a business leader, you can easily gain a clear view of operational performance.
Also, operating income is useful for cost management. It helps you identify where to control costs. A well-documented picture of operating income is necessary for the professionals. It helps make the right decisions related to expense management, production, & pricing strategy. Thus, its role is beyond strategic financial reporting.
Correct data in the operating income statement also enhances credibility with investors and lenders. Such external parties closely analyse the business’s financial health report before investing or securing a loan. Once they find everything upto the mark, the further process becomes smooth.
Get Real-Time Data for Faster Decisions & Stronger Profits
Generate 15+ customized financial reports with real-time data with Moon Invoice.
Last Remarks
Operating income is a crucial component of the financial statement. It demonstrates the company’s true profitability. Therefore, business owners & financial analysts must know how to calculate operating income. Additionally, incorporating the right strategies to enhance the operating profit is another part of the picture. So always manage your operating income wisely when running your business. It is equally important for business owners and investors.